2. Getting Started¶
2.1. Environment Variables¶
The OpenMP Accelerator Model runtime implementation utilizes TI’s OpenCL runtime. It also relies on TI’s C6000 Code Generation Tools version 8.1.x. Set the following environment variables to the correct paths:
-
TI_OCL_CGT_INSTALL¶ The OpenCL runtime is dependent on the C66 DSP compiler product for compilation of OpenCL C kernels. When OpenCL C kernels are compiled on the target ARM/Linux system, the C66 compiler is assumed to be installed in the standard linux locations. However, offline cross compilation of OpenCL C kernels is also supported from x86 Ubuntu machines and in that use case, it is required that this environment variable is set to the top level directory path where the C66 cross compiler tools are installed.
-
TARGET_ROOTDIR¶ Location of target filesystem if cross-compiling on x86/x86-64
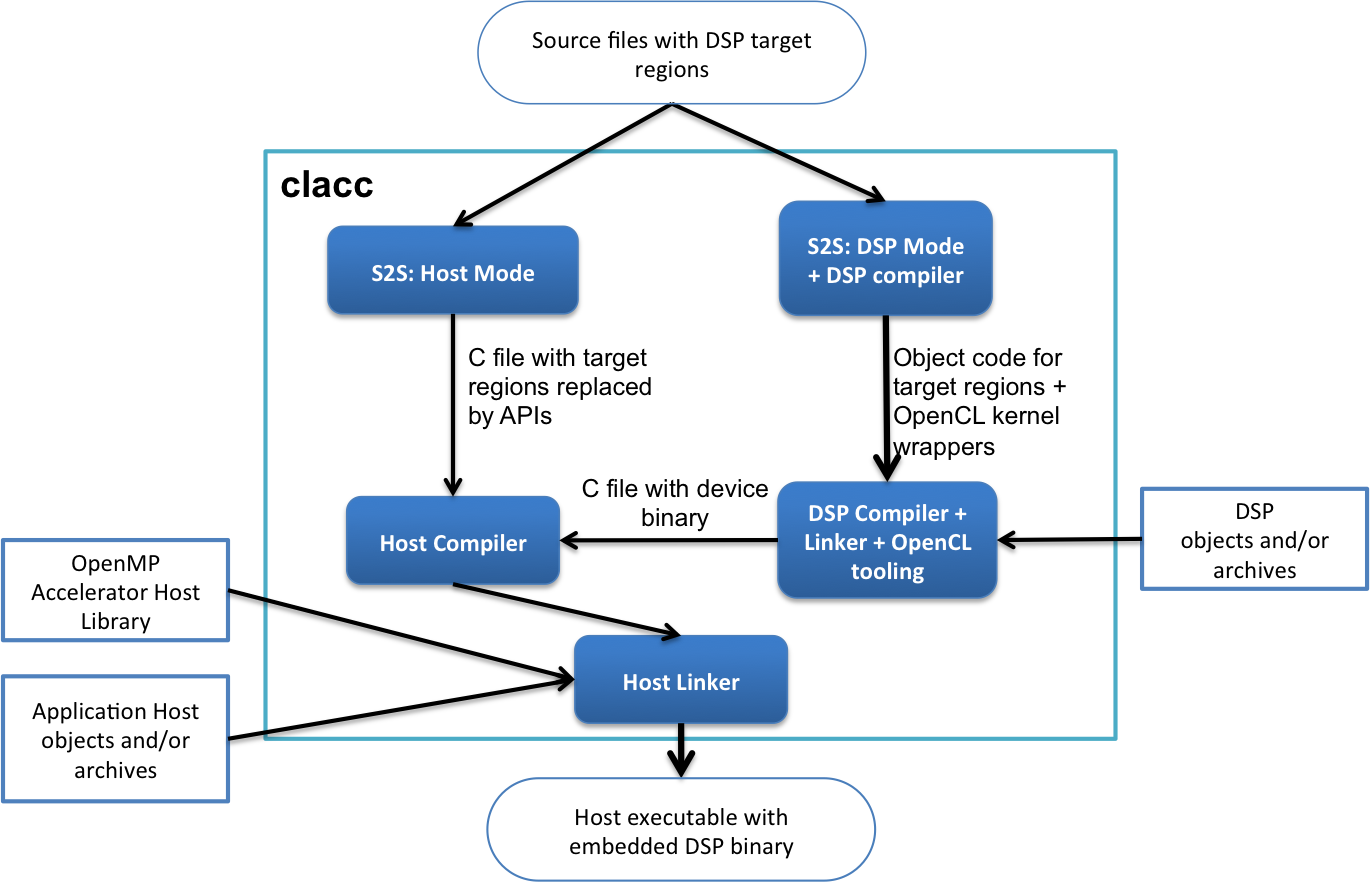
2.2. clacc¶
clacc is a tool used to compile OpenMP 4.0 accelerator model source code. clacc in turn relies on the host gcc toolchain, C6000 Code Generation Tools (CGT) and the TI OpenMP Accelerator Model and OpenCL host libraries.
Building a program using clacc is accomplished with the command:
clacc [options] [object-files] C-source-files
A summary of clacc options are specified below:
| -h, --help | Show help message |
| -v, --verbose | Show debug output |
| -k, --keep_files | |
| Keep intermediate temporary files | |
| -d, --runtime_verbose | |
| Enable runtime debugging information display | |
| -p, --runtime_performance | |
| Enable runtime performance information display | |
| -g, --debug | Generate target debug symbols |
| --make_lib | Make static library |
| --host_cc arg | Host compiler to use |
| --hc arg | Host compiler options |
| --tc arg | Target compiler options |
| --hl arg | Host linker options |
| --tl arg | Target linker options |
| --show_cc_opts | Show host and target compiler options being used |
| -o, --exe | arg Name of executable fat binary |
2.3. Example Applications¶
This product is shipped with a number of examples that demonstrate the use of OpenMP constructs and the TI-specific extensions. The examples typically have the following source directory file structure:
- Host C/C++ file(s)
- File with main() function are named _main.cpp/c
- Files with host equivalents of functions used within target regions are named _host.cpp/c
- Target C file(s)
- Files with #pragma omp target and #pragma omp declare target regions are named _target.c
- Makefile
- Includes a top level make.inc file
At present target regions are only supported in C source files. However, host code may be written in C or C++ and are handled accordingly in the Makefile.
The Makefiles used in the examples have OA_SHELL_OPTS set to -v -k by default, which shows debugging output and does not remove temporary files that are created respectively. After compiling an example the directory may be populated with temporary files: *.out __TI_CLACC_KERNEL.c *.asm *.cl *.dsp_h *.bc *.objc *.if *.map *.opt *.int.c *.o *.obj. Please remove -k option to disable keeping temporary files.
In order to enable display of runtime DEBUG information, add -d flag to OA_SHELL_OPTS
In order to enable display of runtime PERFORMANCE information add -p flag to OA_SHELL_OPTS.
- To compile an example:
$ cd $TARGET_ROOTDIR/usr/share/ti/examples/openmpacc/$ cd vecadd$ make
To run an example:
- Ensure the OpenCL package is installed
- Ensure the OpenMPAcc package is installed
- Ensure the compiled example executable is present on platform file-system
- Run executable
See OpenMP Accelerator Model Examples for brief descriptions of the examples.
2.4. Known Issues & Limitations (v1.1.1)¶
- OpenMP 4.0 device constructs may only be used with C code.
- Only one target device is supported. The target device is a collection of 8 Texas Instruments’ C66x DSP cores.
- Only [lower-bound : length ] syntax for specifying array section is currently supported. See the OpenMP Specification Section 2.4 for more information on array sections.
- The implementation does not support using a target update construct to synchronize variables that are mapped to a device using a declare target construct. However, variables that are mapped to a device using the target data construct may be synchronized using the target update construct.
- When mapping array sections, sections specified in map clauses of an enclosing target data must be replicated in the enclosed target construct for correct behavior.
- OpenMP pragmas may not immediately precede declaration statements. This especially applies to OpenMP point pragmas. For example:
#pragma omp target update from(c[0:size])
int a = 0;
- On 66AK2x, the sum of sizes of all mapped array sections for a single target region must not exceed 1.5 Gb. This is a target DSP device restriction.
- Concurrent target regions are not supported. If host code is multi-threaded, it must be ensured that only one target region is active across the threads. For example, in an OpenMP parallel region, place the target region code in a critical section.
- Any GCC pragmas or attributes in host code compiled using
claccare not retained. - Creating dynamic libraries with target regions using
claccis not supported. - Avoid placing double precision floating point constants in host
source code compiled using
clacc- a loss of precision could occur during source-to-source translation performed byclacc.
2.5. Migration Guide¶
Version 0.3.3 to version 1.1.0
- Modified OMP device construct
#pragma omp declare target endto#pragma omp end declare targetto be consistent with the OpenMP specification, v4.0. - The names and interfaces for the functions used for dynamic memory
management from shared memory have changed.
- __TI_omp_device_alloc() has been replaced with __malloc_ddr() or __malloc_msmc()
- __TI_omp_device_free() has been replaced with __free_ddr() or __free_msmc()
- Changes have been made to
clacccommand options. The changes and additions to the options are listed below. Refer to the section on :ref:<ompa_clacc> for details on updated clacc options.- –lib/-l used to specify host linker options has been replaced with –hl
- –host_cc_opts used to specify host compiler options has been replaced with –hc
- –runtime_debug used to enable runtime debug information has been replaced with –runtime_verbose
- –target_cc_opts used to specify host compiler options has been replaced with –tc
- –lib_path and –inc_path are no longer supported. Compiler and and linker include paths may be specified using –lib and –hc/–tc.
- New option –debug/-g has been added and may be used to generate target debug symbols
- New option –make_lib has been added and may be used to create a clacc static library
- New option –tl has been added and may be used to specify target linker options